Partners contributed to more equitable funding of schools via the Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF)
Passage of Prop 30 and the Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF)
- Directed increased funds to the state’s highest-need districts and students via historic legislation using an equity-based formula.
- Represented a culmination of over a decade of work by grassroots and professional advocates.
-
Helped catalyze this policy change through continued and long-term investment in capacity building of grassroots and statewide advocacy groups and coalitions.
LCFF Implementation
- Ensured parents and students had voice in how funds were allocated to highest-need schools to support low-income students, English Learners, and foster care students to close the achievement gap.
- Democratized parent and student involvement and engagement throughout state.
- Surfaced key challenges surrounding opaque district budgets and varied willingness to share budgetary decision-making.
BHC leaders successfully implemented LCFF and held districts accountable
LCFF implementation & collaboration
West Contra Costa County Unified School District increased base funding in school-based health services from $900k in the 2017-18 school year to more than $1.125M the following school year using Local Control and Accountability Plan (LCAP) funding.
Merced Union High School District allocated $1M from the Local Control Accountability Plan (LCAP) to hire nine new foster and homeless youth education liaisons.
As part of LCAP, $1.9M added to budget for foster youth in the district.
Successfully advocated for LAUSD to implement funding using a Student Equity Needs Index, and to alter its proposed Local Control Funding Formula (LCFF) budget by removing $13M for school police and allocation an additional $2M for restorative justice.
LCFF accountability efforts
West Contra Costa County Unified School District settled lawsuit with parents to release performance and LCAP data.
District settled lawsuit with parents and advocates, promising to pass new school discipline policies, provide teacher training to mitigate implicit bias.
Long Beach Unified School District agreed to invest approximately $7M in additional social emotional and academic supports for high need students as a result of a Un‹form CompIaint Procedure filed by Long Beach parents and organizations.
BHC and CVUSD developed and entered into an MOU to work in partnership to develop LCFF and Restorative Justice public awareness campaign utilizing strategic communication supports.
BHC partners also contributed to a 50% decrease in suspension rates…
In School and Out of School Suspensions
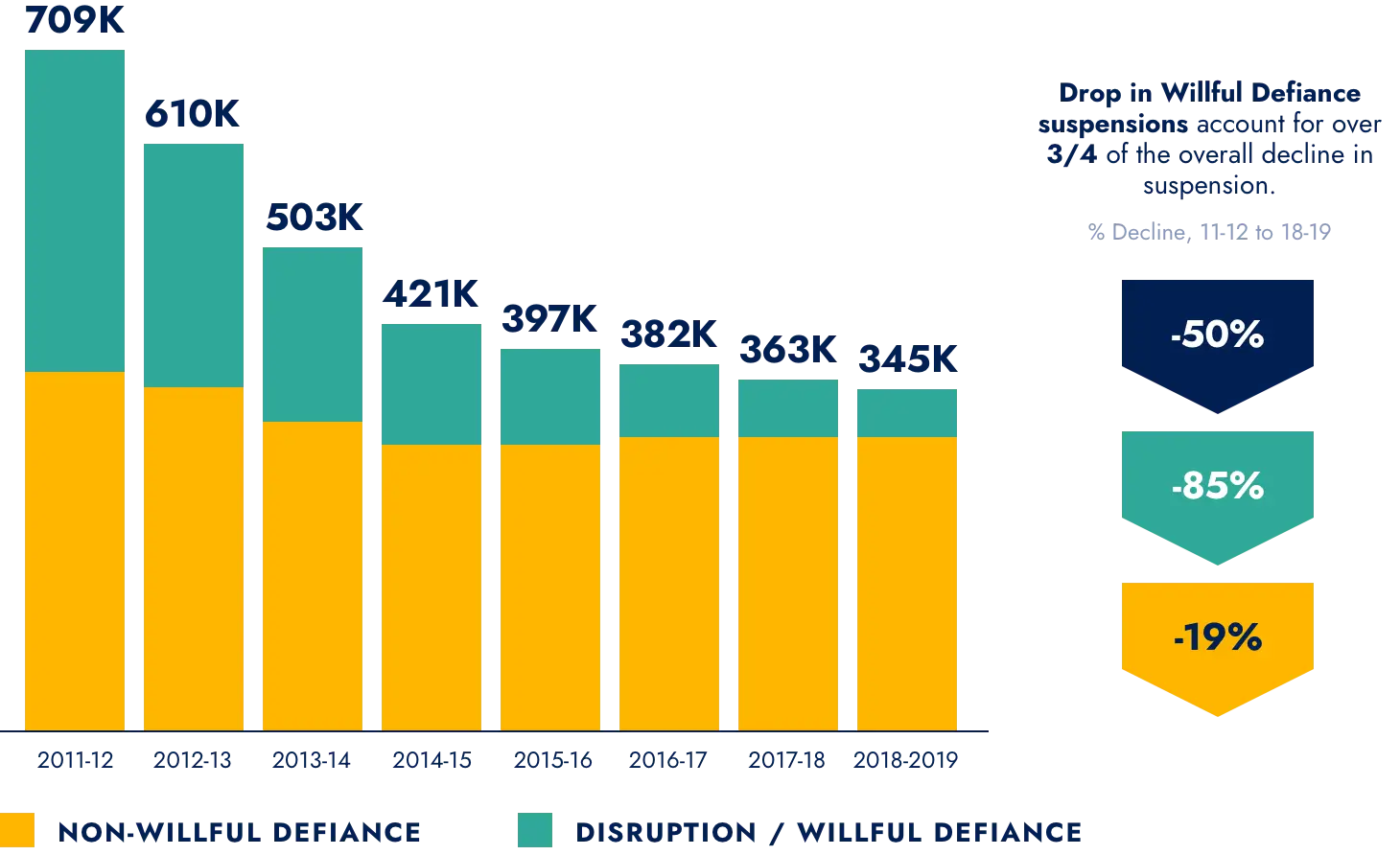 Note: These numbers represent unduplicated suspension events not toal days suspended.
Note: These numbers represent unduplicated suspension events not toal days suspended. Source: CA Department of Education website; Analysis by Tia Martinez, 2019.

Partners helped transform the public narrative
surrounding harsh school discipline by calling attention to systemic challenges and potential solutions
School-to-prison pipeline

Lost Days of Classroom Instruction
Despite a recent decline in the use of suspension in California schools, many students are still losing a great deal of instruction time due to school discipline; Research estimates more than 840k days of instruction were lost during the 2014-15 school year alone.
In California’s 25 districts with the highest suspension rates, the disruption/defiance category contributed to 45% of lost instruction, well above the statewide average of 30%.
Alternatives such as restorative justice, healing, and other trauma-informed practices
Restorative justice (RJ) is a broad term that:
Encompasses a growing social movement to institutionalize non-punitive, relationship-centered approaches for avoiding and addressing harm, responding to violations of legal and human rights, and collaboratively solving problems.
Has been used in schools to address the root causes of harmful behavior and to find solutions that make it right for all parties involved without the student losing class time.
Serves as a means to divert people from traditional justice systems and as a program for convicted offenders already supervised by the adult or juvenile justice system.
BHC partners supported a school climate movement
through policy change and public investment at the state- and local-levels
Statewide Policy
AB 420 (2014): Eliminated “willful defiance” suspensions & expulsions for K-3 students.
SB 1111 (2014): Required due process protections for students transferring to and from alternative schools (e.g. community day schools).
State accountability system (2016): State Board of Education adopted accountability system that incl. suspension rates & chronic absenteeism as two of the six key indicators for measuring school performance.
Teacher credentialing policy (2016): Commission on Teacher Credentialing (CTC) required training in positive discipline practices as restorative justice.
SB 419 (2019): Expanded elimination of willful defiance to middle school and charter school students – law takes effect in July 2020.
Note: The policy changes identified here reflect accomplishments championed by BHC participants during the intiative, but not necessarily with TCE funds. All TCE grants to BHC participants were made in compliance with the requirements of federal tax law.
Source: BHC Policy Inventory Tool, 2020.
AB 420 (2014): Eliminated “willful defiance” suspensions & expulsions for K-3 students.
SB 1111 (2014): Required due process protections for students transferring to and from alternative schools (e.g. community day schools).
State accountability system (2016): State Board of Education adopted accountability system that incl. suspension rates & chronic absenteeism as two of the six key indicators for measuring school performance.
Teacher credentialing policy (2016): Commission on Teacher Credentialing (CTC) required training in positive discipline practices as restorative justice.
SB 419 (2019): Expanded elimination of willful defiance to middle school and charter school students – law takes effect in July 2020.
Note: The policy changes identified here reflect accomplishments championed by BHC participants during the intiative, but not necessarily with TCE funds. All TCE grants to BHC participants were made in compliance with the requirements of federal tax law.Source: BHC Policy Inventory Tool, 2020.
Local Policy
South Sacramento (2011): SCUSD adopted an anti-bullying policy to better support students particularly LGBTQ students; a new position, Bullying Prevention Specialist was created.
South LA/Boyle Heights (2012): LAUSD passed School climate bill of Rights, which eliminated willful defiance as a suspendable offense.
Fresno (2017): School District Board allocated $3.4M in the 2017-18 LCAP for the Student Voice Initiative. The project aimed to create meaningful opportunities for youth voice in school with a focus on underrepresented youth.
East Oakland (2018): J4OS won the removal of a provision from the Board Policy 6066 that would have allowed the district to give $10M of Measure G money (that was explicitly won for in-district schools) to the charter schools that discriminated against and excluded African American and special education students.
Note: The policy changes identified here reflect accomplishments championed by BHC participants during the intiative, but not necessarily with TCE funds. All TCE grants to BHC participants were made in compliance with the requirements of federal tax law.
Source: BHC Policy Inventory Tool, 2020.
South Sacramento (2011): SCUSD adopted an anti-bullying policy to better support students particularly LGBTQ students; a new position, Bullying Prevention Specialist was created.
South LA/Boyle Heights (2012): LAUSD passed School climate bill of Rights, which eliminated willful defiance as a suspendable offense.
Fresno (2017): School District Board allocated $3.4M in the 2017-18 LCAP for the Student Voice Initiative. The project aimed to create meaningful opportunities for youth voice in school with a focus on underrepresented youth.
East Oakland (2018): J4OS won the removal of a provision from the Board Policy 6066 that would have allowed the district to give $10M of Measure G money (that was explicitly won for in-district schools) to the charter schools that discriminated against and excluded African American and special education students.
Note: The policy changes identified here reflect accomplishments championed by BHC participants during the intiative, but not necessarily with TCE funds. All TCE grants to BHC participants were made in compliance with the requirements of federal tax law.Source: BHC Policy Inventory Tool, 2020.
Public Investment
Statewide (2016): A one-time allocation of $30M in statewide school climate funds
Santa Ana (2016): U.S Department of Education awarded Santa Ana Unified School District a $1M grant over 3 years for innovative practices that in integrating socio-emotional practices that reduce suspensions and expulsions.
Del Norte (2017): Del Norte Unified School District won state funding to implement educational equity as the center of Multi-Tiered Systems of Support Implementation (MTSS) to better align initiatives and resources within the district to address the needs of all students.
Statewide (2018): Governor budget set aside $13M for parent engagement.
Statewide (2019): State of California allocated to $15M to support the connections between the Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS) framework and school discipline practices.
Note: The policy changes identified here reflect accomplishments championed by BHC participants during the intiative, but not necessarily with TCE funds. All TCE grants to BHC participants were made in compliance with the requirements of federal tax law.
Source: BHC Policy Inventory Tool, 2020.
Statewide (2016): A one-time allocation of $30M in statewide school climate funds
Santa Ana (2016): U.S Department of Education awarded Santa Ana Unified School District a $1M grant over 3 years for innovative practices that in integrating socio-emotional practices that reduce suspensions and expulsions.
Del Norte (2017): Del Norte Unified School District won state funding to implement educational equity as the center of Multi-Tiered Systems of Support Implementation (MTSS) to better align initiatives and resources within the district to address the needs of all students.
Statewide (2018): Governor budget set aside $13M for parent engagement.
Statewide (2019): State of California allocated to $15M to support the connections between the Multi-Tiered Systems of Support (MTSS) framework and school discipline practices.
Note: The policy changes identified here reflect accomplishments championed by BHC participants during the intiative, but not necessarily with TCE funds. All TCE grants to BHC participants were made in compliance with the requirements of federal tax law.Source: BHC Policy Inventory Tool, 2020.
Partners may have had a measurable impact on school climate and graduation
- At the beginning of the BHC initiative, both suspension and graduation indicators were more negative within BHC communities than the state sample. Six years later, the differences had narrowed.
- There were statistically significant decreases in suspension rates between 2011-12 and 2016-17 among botch BHC Schools and the State Sample, but the decrease was significantly greater among the BHC Schools.
- BHC School Districts experienced an 18 percent growth in graduation rates from school year 2009-10 to 2015-16 compared to the state average of 12 percent.
Four-Year Adjusted Graduation Rates
Graduation rates improved slightly in recent years, through disparities persist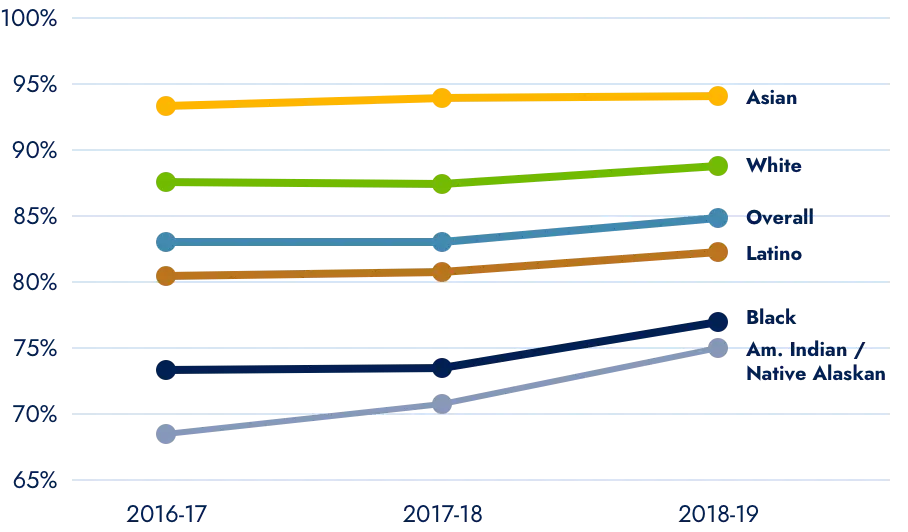
More About Health Happens in Schools
Statewide Context Timeline
Click here for a digital timeline that highlights the statewide context, contributions, and policy changes informed and supported by our Building Healthy Communities partners that are connected to the 2010-2020 BHC Dashboard Summary.
BHC Communities Interactive Map
Click here for a digital map that highlights many local achievements championed by our 14 Building Healthy Community sites that are connected to the 2010-2020 BHC Dashboard Summary.
Unveiling Our 2023 Annual Report
The California Endowment is proud to present our 2023 annual report. Read about the work we are supporting and our partners who are changing California to a state of belonging and inclusion.
View Report

The 2024 Youth Awards Nominations are Closed
Thanks to each of you who took the time to nominate. We are now diligently working on selecting the winners from an incredible pool of nominees. Stay connected for the upcoming announcement.
Learn about the Youth Awards